Reciprocating vs Centrifugal Compressors Explained
Published: 4 Oct 2025
The difference between reciprocating and centrifugal compressors lies mainly in how they work and where they are used. A reciprocating compressor uses a piston that moves up and down to squeeze air, while a centrifugal compressor uses a fast-spinning impeller to push air outward. These two machines may look different, but both play an important role in cooling systems, factories, and everyday appliances.
Let’s move on to our article and discuss it in detail. Are you ready? Let’s see.
Definition of Compressor
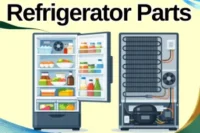
A compressor is the heart of cooling and air systems. It squeezes air or gas to increase pressure and move it through the system.
- It pumps refrigerant (cooling gas) or air inside machines.
- It keeps systems cool by moving gas between coils or parts.
- It makes the gas highly pressurized for better performance.
- Without it, cooling and air systems cannot work.
- Example: Just like a heart pumps blood in our body, a compressor pumps gas in a cooling system.

👉 If you want to read this in detail, our article is here. What is a compressor of a refrigerator?
What is a Reciprocating Compressor
A reciprocating compressor uses a piston that moves up and down to compress air or gas inside a cylinder.
- It works like a bicycle pump that pulls in air and then pushes it out under pressure.
- The piston moves down to draw in gas and moves up to squeeze it tightly.
- This back-and-forth action makes the gas highly pressurized.
- It is strong and can handle heavy loads easily.
- Commonly used in refrigerators, air conditioners, and small industries.
- Example: Just like you pump air into a tire using a hand pump, a reciprocating compressor pushes gas through the cooling system.

What is a Centrifugal Compressor
A centrifugal compressor uses a fast-spinning wheel called an impeller to move and pressurize air or gas.
- It works by spinning air quickly and pushing it outward through centrifugal force.
- The impeller’s speed increases the pressure of the gas smoothly.
- It runs quietly with less vibration and fewer moving parts.
- Commonly used in large air-conditioning systems, factories, and jet engines.
- It provides steady airflow and works well for big cooling needs.
- Example: Just like water moves outward when you spin a bucket fast, a centrifugal compressor pushes air outward to build pressure.

Now that we have learned about these two compressors, let’s see their comparison in the next section.
Comparison Between Reciprocating and Centrifugal Compressors
Both reciprocating and centrifugal compressors do the same job-compressing air or gas-but they work in very different ways. Their design, working style, and performance make each one better for specific uses. The table below shows the key differences between them in a simple way.
Reciprocating vs Centrifugal Compressors Table:
| Feature | Reciprocating Compressor | Centrifugal Compressor |
| Working Style | Uses a piston that moves up and down to compress gas. | Uses a fast-spinning impeller to push gas outward. |
| Operation Type | Works in short strokes, creating pressure in steps. | Works continuously with smooth airflow. |
| Noise Level | Louder because of piston movement. | Quieter and smoother due to the spinning motion. |
| Cooling Efficiency | Handles heavy loads but is less efficient overall. | More energy-efficient with steady cooling. |
| Size | Smaller and fits in compact systems. | Larger and used for big applications. |
| Maintenance | Needs more care due to moving parts. | Requires less maintenance and is easier to manage. |
| Durability | Very strong and reliable for tough use. | Long-lasting with proper handling. |
| Cost | More affordable and found in budget models. | Costlier but offers high efficiency. |
| Best For | Small setups like refrigerators or workshops. | Big systems like factories or central AC units. |
Let’s discuss all the points discussed in the table in detail. Are you ready? Let’s start.
Working Style
Both compressors work differently to pressurize gas, and this difference affects their performance.
- A reciprocating compressor uses a piston that moves up and down inside a cylinder.
- The piston pulls in gas when it moves down and compresses it when it moves up.
- The process happens in small strokes, creating pressure step by step.
- It works like a hand pump that pushes air into a ball or tire.
- A centrifugal compressor uses a spinning impeller (a fan-like wheel).
- As the impeller spins, it throws air outward using centrifugal force.
- This creates a continuous flow of pressurized gas.
- It’s like spinning water in a bucket and watching it move outward.
Operation Type
The way both compressors operate determines how steady and smooth the airflow is.
- The reciprocating compressor works in cycles -suction, compression, and discharge.
- It creates pressure in small steps rather than in a continuous flow.
- This can cause small pulses or jerks during operation.
- The centrifugal compressor runs continuously.
- It pushes air without stopping, giving a smooth and even flow.
- Because of this, it’s more suitable for large systems that need a steady air supply.
Noise Level
Noise is one of the easiest ways to notice the difference between the two.
- A reciprocating compressor is noisier because of the piston’s up-and-down motion.
- The repeated strokes create vibration and mechanical sounds.
- Over time, it may sound like a soft knocking or humming.
- A centrifugal compressor is much quieter.
- It spins smoothly, with fewer parts moving back and forth.
- That’s why it’s mostly used in large buildings where quiet operation matters.
Cooling Efficiency
Cooling efficiency depends on how well a compressor handles load and power use.
- A reciprocating compressor produces high pressure but lower airflow.
- It works great under heavy cooling loads – like when the system runs nonstop.
- However, it uses more energy because of its piston motion.
- A centrifugal compressor produces high airflow with steady pressure.
- It uses less electricity and gives balanced cooling.
- It’s ideal for big air-conditioning systems that run all day with fewer fluctuations.
Size
The physical size of the compressor also affects where it can be used.
- Reciprocating compressors are smaller and compact.
- They fit well in small machines like refrigerators and small AC units.
- Their design is simple and easy to install in tight spaces.
- Centrifugal compressors are larger and heavier.
- They are made for big industrial systems or central cooling units.
- They need more space and a stable setup to run efficiently.
Maintenance
Every machine needs care, but the amount of maintenance depends on the design.
- Reciprocating compressors have more moving parts – pistons, valves, and rods.
- These parts wear out faster, so they need regular checks and lubrication.
- Over time, they may need more repairs.
- Centrifugal compressors have fewer moving parts.
- They run with less friction and need less maintenance.
- However, if a problem occurs, it may require expert help because of the complex design.
Durability
Durability shows how long the compressor can last with regular use.
- Reciprocating compressors are strong and built for heavy-duty work.
- They can handle frequent starts and stops easily.
- Even in hot weather or heavy loads, they perform well.
- Centrifugal compressors are also durable but need clean conditions and proper handling.
- Since they spin at high speed, dirt or imbalance can reduce lifespan.
- With proper care, they can last for many years in large systems.
Cost
Cost is an important factor when choosing the right compressor.
- Reciprocating compressors are cheaper to make and buy.
- That’s why they’re common in small refrigerators and air conditioners.
- They give reliable performance at a lower price.
- Centrifugal compressors are more expensive.
- They offer better efficiency and quiet operation, which adds to the cost.
- They are often found in premium or commercial cooling systems.
Best For
Each compressor suits a different need depending on size, cost, and performance.
- Reciprocating compressors are best for small systems and tough working conditions.
- Ideal for refrigerators, workshops, or places with frequent power cuts.
- They’re great where strong cooling and durability matter most.
- Centrifugal compressors are best for large systems needing smooth, steady airflow.
- Perfect for big factories, malls, or central AC systems.
- They’re ideal for users who want quiet performance and energy savings.
Which One Should You Choose?
Both compressors have their own strengths, but the right choice depends on where and how you plan to use them. Let’s make it easy to decide.
- If your main goal is steady cooling in large spaces like factories, shopping malls, or big offices, a centrifugal compressor is the better choice. It runs smoothly, saves energy, and keeps air flowing without interruptions.
- If you need a powerful, heavy-duty compressor for smaller setups like workshops, gas stations, or home cooling systems, go with a reciprocating compressor. It’s simple, strong, and works well under tough conditions.
- Think about usage time-centrifugal compressors perform best when running continuously, while reciprocating ones suit systems that stop and start more often.
- Also consider budget and maintenance-reciprocating compressors are cheaper to buy and easier to repair, while centrifugal models cost more but need less frequent servicing.
- In short, choose the one that fits your system size, working environment, and energy needs.
If you’re still a bit confused, these questions and answers will make things clear.
Common Questions About Reciprocating and Centrifugal Compressors
Even after learning the difference between reciprocating and centrifugal compressors, many people still have more questions about how these machines work in real life. These questions help buyers and technicians understand which compressor fits their needs better. Below, we have listed some of the most common questions that people ask about these two types of compressors.
List of Questions:
- Why do centrifugal compressors need high-speed operation?
- Can reciprocating compressors be used for large industrial plants?
- Do both compressors use the same type of refrigerant?
- How does altitude or air pressure affect compressor performance?
- Which compressor type is safer for continuous 24-hour operation?
- How do reciprocating and centrifugal compressors handle moisture or dust?
- Can a centrifugal compressor start instantly like a reciprocating one?
- Which type of compressor gives a more stable air pressure output?
- How do these compressors behave during low-load conditions?
- What type of compressor is more suitable for energy-saving systems?
Now we discuss the answers to all the questions in detail, one by one. Are you ready? Let’s read together.
Centrifugal compressors rely on speed to generate pressure.
- The impeller spins very fast to throw the air outward using centrifugal force.
- The higher the speed, the greater the pressure of the gas.
- This speed creates smooth and continuous airflow, unlike the stepwise motion of reciprocating compressors.
- That’s why centrifugal compressors usually work with motors or turbines designed for high RPM (revolutions per minute).
Reciprocating compressors can work in industries, but only for limited purposes.
- They are suitable for smaller industrial processes that require high pressure but low air volume.
- Large plants prefer centrifugal compressors because they can handle large air volumes continuously.
- Using a reciprocating compressor in big systems would require multiple units, increasing maintenance and cost.
No, refrigerant choice often depends on the compressor design and purpose.
- Reciprocating compressors use a wide range of refrigerants, like R-134a, R-22, or R-290.
- Centrifugal compressors usually use refrigerants suited for high-capacity systems like R-1233zd(E) or R-134a.
- Choosing the wrong refrigerant can affect efficiency, safety, and pressure levels.
Altitude plays an important role in how compressors perform.
- At higher altitudes, air pressure and density are lower.
- For reciprocating compressors, this means they take in less air per stroke, reducing output.
- Centrifugal compressors also face reduced efficiency, but can adjust better with speed control or design changes.
- Engineers usually derate compressors (reduce their capacity) when used in high-altitude locations.
Centrifugal compressors are more suited for continuous operation.
- They have fewer moving parts, which means less wear and tear.
- They run smoothly without generating heavy vibration or noise.
- Reciprocating compressors can overheat if used nonstop without rest, especially under high loads.
- For round-the-clock cooling or air supply, centrifugal systems are the safer and more efficient choice.
Moisture and dust can damage compressors if not handled properly.
- Reciprocating compressors are more sensitive because their pistons and valves can get blocked or rusted.
- Regular filters and dryers are needed to protect them.
- Centrifugal compressors, on the other hand, handle dust better because of smoother airflow and an enclosed design.
- However, they still need clean air filters to maintain performance.
Not exactly. Centrifugal compressors take time to reach operating speed.
- They need gradual acceleration to avoid mechanical stress on the impeller.
- Reciprocating compressors can start instantly since their pistons move directly with motor power.
- However, advanced centrifugal models use “soft-start” systems to reduce delay and protect internal parts.
Centrifugal compressors provide smoother and more stable air pressure.
- Their continuous flow reduces fluctuations.
- Reciprocating compressors, due to their piston strokes, deliver pressure in pulses.
- This makes centrifugal compressors ideal for systems that need consistent airflow, like central AC or industrial cooling systems.
Compressor performance changes when the system demand is low.
- Reciprocating compressors can easily start and stop to match load changes.
- Centrifugal compressors may face “surge” problems if not properly controlled during low-load operation.
- To prevent this, engineers use variable-speed drives or control valves in centrifugal systems.
Centrifugal compressors are usually better for energy efficiency.
- They offer high efficiency at full load and even at partial load with variable-speed drives.
- Reciprocating compressors consume more power because of their piston motion and friction.
- However, in small systems or where the budget is tight, reciprocating compressors can still be a cost-effective option.
Conclusion
So, guys, in this article, we’ve covered the difference between reciprocating and centrifugal compressors in detail. Both have their own strengths-reciprocating compressors are great for smaller systems and heavy-duty work, while centrifugal ones shine in large, continuous operations. Personally, I’d recommend a centrifugal compressor if you want smooth, energy-efficient cooling for big setups. But for compact machines like home refrigerators or workshops, a reciprocating compressor works perfectly.
If you want to explore more about Types of refrigerator compressors, you can read our detailed guide!